
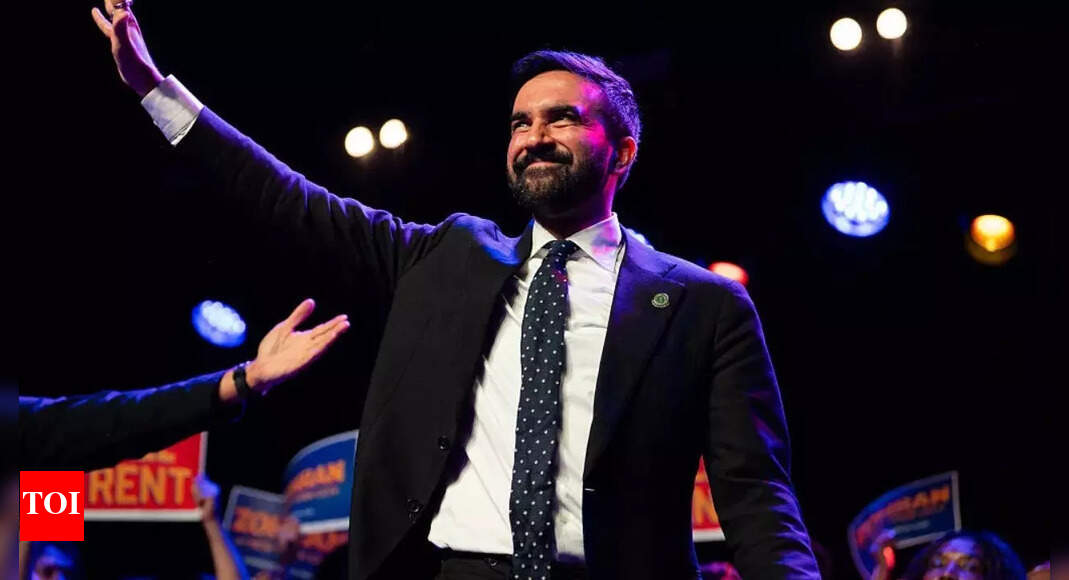
As Zohran Mamdani positions himself for one of the most consequential roles in American municipal governance, the mayoralty of New York City, his political philosophy is being examined not only for its content but also for the intellectual tradition from which it emerges.
A democratic socialist with deep grassroots ties and a precise policy instinct, Zohran’s approach to power is shaped not just by conviction but by inheritance. This inheritance is not merely biological; it is profoundly intellectual. At the heart of that legacy stands his father, Mahmood Mamdani, a political thinker shaped by exile, rooted in anti-colonial critique, and internationally renowned for reshaping how the world understands state authority and postcolonial governance.
Here is the story of his education and career—the foundation that has indelibly shaped his son’s political consciousness.
Mahmood Mamdani’s academic journey: How a student of struggle became a scholar of power
Mahmood Mamdani’s academic journey is as compelling as his scholarship. Born in 1946 in Bombay and raised in Kampala by Gujarati Muslim parents, his early years were marked by constant movement across East Africa and growing political awareness. Selected as part of the historic Kennedy Airlift initiative in the 1960s, he joined a select cohort of East African students who studied in North America during the decolonisation period.
He earned his undergraduate degree in political science from the University of Pittsburgh, where his commitment to justice took root through civil rights activism. After participating in protests in Montgomery, Alabama, and facing imprisonment for his stance, Mamdani deepened his engagement with revolutionary thought. He went on to complete a Master’s at Tufts University and later obtained a PhD in Government from Harvard, where his dissertation on class and politics in Uganda laid the intellectual foundation for his future work.
Mahmood Mamdani’s career: A life of scholarship forged in struggle
Mamdani’s academic and personal life has been shaped by political upheaval. Shortly after returning to Uganda to conduct doctoral research, he was expelled by Idi Amin for his ethnicity and forced into exile. From the United Kingdom, he moved to Tanzania, joining the University of Dar es Salaam — a crucible for postcolonial thought. Despite being rendered stateless in the 1980s due to his criticism of Milton Obote’s regime, Mamdani continued his work with unrelenting conviction.
He returned to Uganda after Obote’s fall and became the founding director of the Centre for Basic Research, one of the country’s first independent think tanks. His academic career spanned institutions across the globe, including the University of Cape Town, Princeton, and Columbia University, where he currently teaches in the departments of Government, Anthropology, and African Studies.His scholarship remains foundational in the study of colonialism, authoritarianism, and the politics of knowledge.
In his landmark work Citizen and Subject, Mamdani argued that the colonial state in Africa operated through a bifurcated system — one that simultaneously created urban civil power for citizens and rural authoritarian rule over subjects. This analytical framework challenged the conventional understanding of apartheid and extended far beyond South Africa.
His writings continue to inform how academics and policymakers understand the enduring legacies of colonial governance and state violence.
For Zohran Mamdani, these were not distant theories, but lived realities, discussed, debated, and dissected within his own home.
Mahmood Mamdani’s legacy finds its voice in Zohran’s politics
Where Mira Nair offered her son a global lens for storytelling and empathy, Mahmood Mamdani provided him with the intellectual tools to interrogate power and structure. Zohran’s political style — principled yet strategic, radical yet methodical — carries clear echoes of his father’s analytical discipline.
In his advocacy for housing justice, immigrant rights, and racial equity, Zohran channels not only the urgency of social movements but also the clarity of postcolonial critique.
His is a politics informed not just by protest, but by a lifetime immersed in theory, history, and the study of systems that marginalise and exclude.
In a political age often defined by spectacle and short-termism, Zohran Mamdani’s approach stands apart. It is grounded in an education shaped by two of the most dynamic thinkers of their generation. Mahmood Mamdani did not simply shape academic discourse — he cultivated a worldview in his son that merges scholarship with service, resistance with reform, and vision with action. The intellectual lineage that Zohran carries into public life is not just an inheritance; it is a compass.

 10 hours ago
50
10 hours ago
50






















 English (US)
English (US)