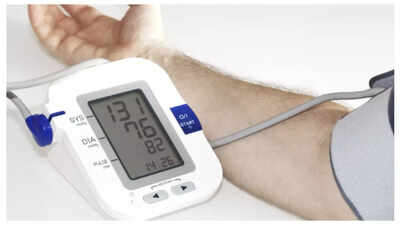
Blood pressure
is the force of circulating blood against the walls of your arteries. It's measured in millimeters of mercury (
mm Hg
) and is usually expressed as two numbers: systolic pressure (top number, pressure when the heart beats) and diastolic pressure (bottom number, pressure between beats). Blood pressure can greatly vary, and can present itself as high blood pressure (hypertension), or low blood pressure (hypotension). While both conditions can result in health issues, a minor case of low bp is usually not of much concern, however those suffering from high bp need to always monitor their bp.
In healthy individuals, blood pressure is typically considered to be less than 120/80 mm Hg, though this can vary with age. High BP is known to be the starting point of many lifestyle ailments like heart diseases, stroke, and others, hence it is imperative to keep your BP in check...

What factors can effect your blood pressure?
Heart rate: A faster heart rate can increase blood pressure.
Artery size: Narrower arteries increase blood pressure.
Blood volume: More blood volume increases blood pressure.
Artery elasticity: Stiffness in the arteries can raise blood pressure.
Stress: Stressful situations can temporarily raise blood pressure.
Age: Blood pressure generally increases with age.
Medications: Certain medications can affect blood pressure.
Diet: A high-sodium diet can raise blood pressure.
Exercise: Regular exercise can help lower blood pressure.
Weight: Obesity is a risk factor for high blood pressure.
High blood pressure (hypertension) is a condition where blood pressure consistently measures 130/80 mm Hg or higher. It's often referred to as the "silent killer" because it usually has no noticeable symptoms until complications arise.
Low blood pressure (hypotension) is a condition where blood pressure is consistently low, generally less than 90/60 mm Hg. If chrnoic, it can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting.
Understanding Manual Blood Pressure Machines
Manual BP machines (the one you see at hospitals) use a cuff, a bulb to inflate it, and a stethoscope to listen to blood flow sounds (
Korotkoff
sounds) as the cuff pressure is slowly released. The healthcare professional notes the systolic and diastolic pressures by hearing these sounds.
Accuracy and Advantages
Manual BP machines, especially mercury sphygmomanometers, are considered the gold standard for accuracy when used correctly by trained professionals.
They provide precise measurements because they rely on direct auscultation, allowing detection of subtle changes and irregular heartbeats.
Manual devices do not depend on batteries or electronics, reducing the chance of mechanical failure.
They are cost-effective and widely used in clinical settings.

Limitations
Accurate use requires training and skill; improper technique can lead to errors.
The process is slower and less convenient, especially for home use.
Manual measurement can be influenced by environmental factors and if the patient is experiencing anxiety, sometimes resulting in higher readings.
Not ideal for self-monitoring without assistance.
Understanding
Digital
Blood Pressure Machines
Digital BP machines automatically inflate the cuff and use electronic sensors to detect blood flow, displaying results on a digital screen. They are found in mostly all homes now, and are extremely easy to operate.
Accuracy and Advantages
Digital monitors are user-friendly and require no training, making them ideal for self-monitoring at home.
They provide quick readings and often include memory functions to track blood pressure over time.
Many models display pulse rate and have large, clear screens.
Studies show digital monitors have a moderate to high accuracy level, with pooled sensitivity around 79% and specificity about 91% compared to mercury sphygmomanometers.
They reduce human error in reading results and cuff inflation.
Limitations
Digital devices may give inaccurate readings in 5 to 15 percent of people due to factors like incorrect cuff size, movement, or irregular heart rhythms.
They may struggle to detect arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats as accurately as manual devices.
Some models can be expensive and require battery power.
Accuracy can be affected by improper cuff placement or user error.
Ideally, an average of 3 readings is what is recommened by doctors when it comes to digital devices.
Comparing Accuracy: Which Is More Reliable?
Manual devices are more accurate when used properly because they allow healthcare professionals to listen directly to blood flow sounds and adjust technique as needed.
Digital devices provide convenience and reasonable accuracy but can sometimes miss subtle variations or irregular rhythms.
In clinical settings, manual measurement remains the reference standard, especially for critical patients, because it can detect higher blood pressure readings that digital devices might underestimate.
For routine home monitoring, digital devices are widely accepted and recommended due to ease of use and good overall accuracy.
Why Does Accuracy Matter?
Accurate blood pressure measurement is essential for diagnosing hypertension, deciding treatment, and monitoring progress. Inaccurate readings can lead to misdiagnosis, unnecessary medication, or missed treatment opportunities. Manual devices, with their precision, are preferred in hospitals and clinics, while digital devices empower patients to monitor their health conveniently at home.
Which Should You Choose?
Choose a manual BP machine if:
You are a healthcare professional or trained user seeking the highest accuracy.
You want to detect irregular heartbeats or need precise readings in critical care.
You prefer a cost-effective and durable device.
Choose a digital BP machine if:
You want a simple, quick, and easy-to-use device for home monitoring.
You prefer automatic inflation and digital display for convenience.
You want to track your readings over time with memory functions.
Both types have their place in managing hypertension. Digital monitors have improved significantly and offer sufficient accuracy for most people, especially for regular home use. However, manual devices remain the gold standard in clinical settings due to their precision and reliability.

 2 months ago
173
2 months ago
173























 English (US)
English (US)