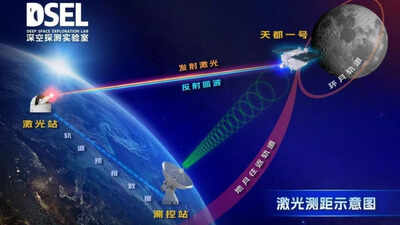
Chinese scientists have made a groundbreaking achievement in space exploration by successfully conducting satellite lasers ranging in the Earth-moon space during the day, overcoming the strong daylight interference.According to Li Yuqiang, a researcher at Yunnan Observatories, the research team successfully beamed a laser to the
Tiandu-1 satellite
, approximately 130,000 kilometers away from the Earth, and captured the return signal using a newly upgraded near-infrared lunar laser ranging system of an 1.2 meter telescope. This achievement enhances navigation and positioning capabilities in the Earth-moon space, supporting future
deep-space exploration
projects.
China’s groundbreaking daytime laser signal to Tiandu-1 satellite
This experiment, conducted on April 26-27, marked the first-ever daytime Earth-to-moon laser-ranging trial. According to xinhuanet.com, China’s Deep Space Exploration Laboratory successfully fired a precision laser from Earth to the Tiandu-1 satellite, approximately 130,000 kilometers away, with the signal returning despite strong sunlight interference. Researchers at the Yunnan Observatories of the
Chinese Academy of Sciences
, said, it marks a significant breakthrough in precise deep-space orbit measurement. Previously, limited to night time due to sunlight interference, the technology achieved centimeter-level accuracy, setting a new standard for future space operations. This advancement is seen as a significant step toward China’s planned crewed lunar mission by 2030.
Breakthrough by China
This accomplishment in laser ranging will improve the lunar missions of China, and exploration of deep space, through precise orbital measurements and communications. This achievement of this experiment also displays China's progress in
lunar navigation
and space communications, providing us with the opportunity to carry out more accurate and frequent missions to the
Moon
and beyond.Also read | Unique rare Earth elements unveiled on an underwater island; here’s what it means for the future

 13 hours ago
30
13 hours ago
30




























 English (US)
English (US)